The world is transforming with the advent of new technologies. It is the age of internet and automation. The extensive use of digital technologies enables data integration faster, smoother, accurate, efficient and more meaningful across machines resulting in enhanced quality products at groundbreaking costs. The phenomenon that the current generation is witnessing is often being termed as Industry 4.0 OR I4 which is the term coined for the trend of automation and digitization of manufacturing, representing the 4th Industrial Revolution. The current trendsetter is expected to take the adoption of computers in 3rd Industrial Revolution a step further by enhancing the system capabilities by comprehending with smart digital autonomous solutions fueled by the Internet of Things and data and machine learning.
Industry 4.0 is aimed to revolutionize the manufacturing processes by incorporating custom and autonomous mass production technologies and make ‘Smart Factory’ an achievable reality. Factories will keep evolving and become smarter with time as they are injected with more data, resulting in enhanced productivity. The interconnected machine network with the capability to interact with manufacturers would lead to a phenomenon called cyber-physical production system (CPPS). This is bound to break the shackles between the real world and the virtual world.
Gordon Styles, president, and CEO of Star Rapid, a provider of rapid prototyping, rapid tooling and low-volume production services, summed up nicely:
“Every now and again, there’s some fundamental shift that happens, then becomes a trend and eventually becomes mainstream. That’s how we got to mechanization and mass production, and now computers and automation. We’re seeing a transition from having machines with computers in isolation to machines with onboard computers that are communicating or being controlled from other computers. And it’s not something that happens overnight—obviously, it’s something that has gradually come about as devices have become more connected.”
Organizations across the globe face a formidable challenge to embrace Industry 4.0 and develop in-house capability and skill to adapt and implement changes today to welcome a sustainable tomorrow. Organizations must prepare themselves by understanding the nitty-gritty of design principles of Industry 4.0. Design principles for Industry 4.0 can be broadly categorized as follows-
- Interoperability and Networking: In order to achieve the objective of the Smart factory, a high level of accurate and timely communication between machines and management is obligatory. Internet of things and digitization is stimulating this need of the hour.
- Simulation: Technological innovation is breaking barriers between real and virtual reality. Simulating the real world into the virtual environment can prove to be a ‘make or break’ for many organizations by enabling them to make decisions in a virtual copy of the surrounding environment and foresee the impact.
- Dynamic Environment: Smart factory must possess the capability to be fed with real-time data, analyze it and make decisions on new findings. This should incorporate sudden disruptions like line failure or defect generation during the production run and thus capability to delegate or fall back on alternate plans. The overall flexibility of the manufacturing process is greatly enhanced.
- Customer Satisfaction: Any advancement cannot be called a success if it is not customer oriented. Organizations and devices must connect to the needs and requirements of the customer and create products as per specifications. Internet of things and the Internet of Services plays a vital role in fulfilling this objective of I4.
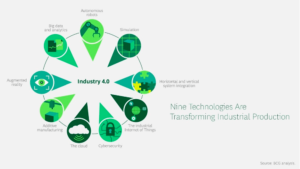
As per the BCG group, following 9 technologies are going to play a pivotal role in Industry 4.0-
-
Autonomous Robots
-
Simulation
-
System Integration
-
Internet of Things
-
Cyber Security
-
The Cloud
-
Additive Manufacturing
-
Big data Analytics
-
Augmented Reality
Advantages of I4:
- Innovation – Industry 4.0 is set to revolutionize modern-day manufacturing by an incepting in-depth understanding of product design and process by accommodating R&D and experimentation paving way for new product design.
- Agility – Built-in intelligence and agility are two key features that Industry 4.0 would introduce in manufacturing.
- Productivity – Automation and digitization being the inherent motive of Industry 4.0 would mean less scope for human error, quick and accurate decision making resulting in high quality and cost-effective product.
- Happy Customer – Real-time data availability would lead manufacturing firms to communicate effectively and efficiently and thus allowing them to serve the customers in a far better way than ever.
- Cost Reduction – Despite initial investment requirement, Industry 4.0 is bound to bring down the production cost by reaping the benefits of machine learning and intelligence.
- Revenue Growth – Combining all the factors, Industry 4.0 can only lead the organizations to success by opening new horizons- market depth and shares, higher margins, exceptional products, better responsiveness towards customers are to name few.
Disadvantages of I4:
- Security Threats – With the emergence of digitization, its apparent IT risks also creeps in. Firms are skeptical about their production line falling prey to any wrongdoing.
- Reliability – Industry 4.0 largely depends on the concept of CPPS wherein effective and stable M2M communication is of utmost importance and thus is under the scanner.
- Initial Investment – Smart Factory is a fascinating term which will cost dearly to the ones pioneering to realize the dream. Thus, it primarily alienates all small and medium firms and might force bigger firms to reassess the phenomenon.
- Skill Deficiency – There is an absolute scarcity of skill set in the market in this domain. Companies would have to struggle initially to develop the requisite skill set internally or make efforts to hire from outside.
- Absence of Regulation – The phenomenon of Industry 4.0 is a novice and lacks maturity. Hence, a close watch is the need of the hour. However, the market lacks any form of regulation, standard or certification to keep an eye on the development.
- Job Cuts – With the adoption of automation in the production line, job losses are inevitable initially and will hamper early acceptance. But with time, Industry 4.0 would open doors for new skill sets and job opportunities.
Thus, in principle, Industry 4.0 is truly mesmerizing and enables mankind to look beyond physical limitations. Optimizing the production, flexibility in manufacturing which is customer-oriented and providing a new realm for new skill sets and job opportunities- are few advantages attributable to Industry 4.0. However, one cannot oversee the data and cybersecurity risks that are inherent along with the huge capital investment required to set up the Smart Factory. This will not only alienate the SMEs from this revolutionary phenomenon but even the slightest miscalculated risk for the bigger organization can cost them their market shares. Thus, large corporations backed by the governments must invest in tackling the challenges by pursuing the R&D and experimentation in order to make Industry 4.0 a big success for forthcoming generations.
About the Author

Ashutosh Sahu has 6+ years of rich experience in Oracle VCP and Cloud applications, Ashutosh is a qualified MBA in Industrial and Supply Chain Management. His focus areas are advisory and solutions consulting for a range of Supply Chain organizations.